
Campus Moncloa
Campus of International Excellence
Devonian
419-359 M.a.
British geologists identified this period in the nineteenth century from rocks in Devon County (UK).
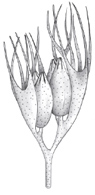
First Archaeosperma seeds (Gymnosperm).
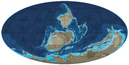
Laurentia and Baltica are still colliding during this period while Gondwana continues to break up: two large continental fragments split from its edge which today form part of China.
This is a time of warm climate in which the first forests appear. Ferns and the first seed plants appear at the end of this period.
The seas become populated with larger, more complex and diverse organisms; rich ecosystems of algae, corals, molluscs, echinoderms and primitive fish are formed. Early tetrapods, the ancestors of terrestrial vertebrates, evolve from fleshy-finned fish in shallow waters. At the end of this period a new extinction occurs that particularly affects shallow-water species and wipes out many of these tetrapods.

Devonian marine animals.
| Hadean | ~4600-4000 M.a. |
| Archean | 4000-2500 M.a. |
| Proterozoic | 2500-541 M.a. |
| Cambrian | 541-485 M.a. |
| Ordovician | 485-443 M.a. |
| Silurian | 443-419 M.a. |
| Devonian | 419-359 M.a. |
| Carboniferous | 359-299 M.a. |
| Permian | 299-252 M.a. |
| Triassic | 252-201 M.a. |
| Jurassic | 201-145 M.a. |
| Cretaceous | 145-66 M.a. |
| Paleogene | 66-23 M.a. |
| Neogene | 23-2,6 M.a. |
| Quaternary | 2,6 M.a.-act. |
